Gasteroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Heavy drinking of alcohol and smoking
- Hiatal hernia (part of your stomach moves above the diaphragm; the diaphragm is the muscle separating your chest and the cavities of the abdomen)
- Overweight and obesity
- Use of certain medications for conditions like asthma, depression, anxiety, high blood pressure.
- Pregnancy
- Scleroderma
- Overeating or failure to eat small frequent meals
- Consumption of caffeine, tomato based foods, fatty foods etc
- Nausea (urge to vomit)
- Chest pain
- Wheezing and dry cough
- Difficulty swallowing
- Hoarseness or change in voice
- Sore throat
- Symptoms due to complications- painful swallowing (due to foodpipe ulcer), weight loss (due to narrowing of foodpipe), weakness or fatigue due to blood loss. Black tarry stool or vomiting blood.
- When symptoms are severe or present for long time
- Symptoms not responding to GERD medicine
- Seek urgent medical care if –
- Chest pain
- Difficulty swallowing or painful swallowing
- Black tarry stool, blood in stool or vomiting blood
- Weight loss
- If you are overweight, you need to lose weight.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol
- Avoid food that worsen symptoms (coffee, carbonated drinks, chocolate fatty and acidic foods)
- Eat small frequent meals slowly
- Do not eat immediately before sleeping, raise headend of bed about 6 inches.
- Indulge into regular exercise and healthy diet
- You can use over-the-counter and prescription GERD treatment drugs, such as
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) that reduce stomach acid like Omeprazole, Pantoprazole
- H2 blockers that decrease the stomach acid like Ranitidine
- Antacids may help mild symptoms for short period of time
- Sometimes you might need an anti-reflux surgery especially if all the above treatments fail. An operation can ‘tighten’ the lower oesophagus to prevent acid leaking up from the stomach.
- Don’t drink alcohol. Don’t smoke.
- Avoid acidic, fatty and spicy food
- Wait 3-4 hours after meal before lying down
- Avoid taking pain relieving medicine such as ibuprofen, or naproxen
- Lose weight, if you are overweight
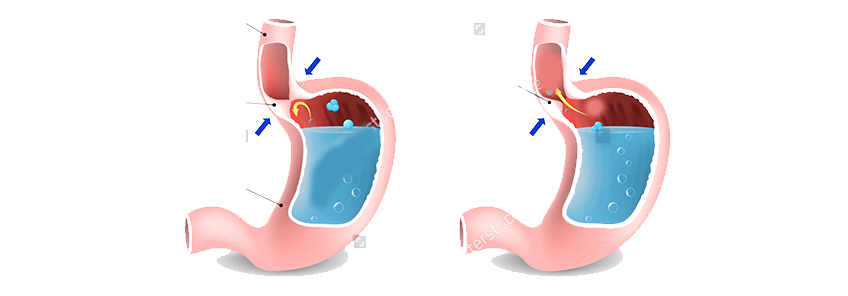
Gasteroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is also known as acid reflux. GERD occurs is when stomach contents leak backwards (called “reflux”) into esophagus and cause symptoms or complications. Reflux is a normal process in infant, child or adult, but when it causes troublesome symptoms it becomes disease.
Weakness of muscles at lower end of esophagus (food pipe) or distension of stomach allows stomach content to back up into esophagus, sometime reaching upto throat or lungs. Chronic acid reflux can cause inflammation of esophagus (esophagitis) leading to stricture (narrowing) or change in its lining (Barrett’s esophagus) which has potential for changing into cancer.
Risk Factors
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of GERD are heartburn (the feeling of burning in your throat or chest) and acid regurgitation (sour taste in the back of your mouth). Symptoms may worsen after heavy meal or when you lie down. Other symptoms may include:
When to seek medical care/Red flags?
Diagnosis
GERD is diagnosed by clinical symptoms alone. Diagnostic test may be needed when patients fail to respond to treatment, when complication due to GERD is suspected or to evaluate for other diagnosis.
Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (EGD): when pts fail to respond to GERD treatment, have difficulty or painful swallowing, are losing weight or have anemia (low hemoglobin)
Tests to evaluate other symptoms – like ECG for chest pain, chest x ay for cough and wheezing, ENT consultation for hoarse voice, Blood test for anemia.
Other specialized tests like acidity (pH) or pressure (manometry) check in food pipe may be required in some cases.
Treatment
The effective treatment of GERD can be done through lifestyle changes, medicine and surgery.
Lifestyle changes:
Medicine:
Surgery:
Prevention
Here are the list of things to avoid GERD:



Send us your feedback on this article