- Unprotected sex
- Multiple sex partners
- HIV infection
- Man who makes sexual relationship with men.
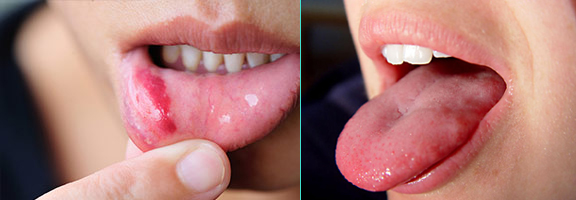
- Primary stage : After Treponema pallidum infection, the primary symptom will manifest with a chancre, usually within 21 days. They look like small circular sores which are painless, called chancre. Such chancres maybe seen inside lips too. Being these chancres usually painless and internal, they can be easily missed by both patients and doctors. Without treatment, a chancre will heal in anywhere from three to six weeks. The chancre contains the infectious bacteria, this stage is highly contagious. Any contact with the chancre can spread the infection.
- Secondary stage : If primary syphilis is left untreated, secondary stage of syphilis may develop. It occurs within 4 to 10 weeks of a primary infection. This stage is characterized by a skin rash on almost any part of the body, including sores inside the mouth, vagina or anus. The copper colored rashes of secondary syphilis is often found on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. Fever, enlarged lymph nodes, fatigue, weight loss, hair loss, headaches, joint aches and muscle aches have been reported in the secondary stage of syphilis. If this secondary stage of the infection is not treated, the infection can progress to tertiary stage of syphilis which is very complicated and severe. But sometimes, syphilis will show no symptoms at all, which is called latent syphilis.
- Tertiary stage : The last stage of infection is known as tertiary syphilis. It is the most serious stage of infection. It’s characterized by major diseases of the skin, bones, heart, liver, and other organs. Neurosyphilis, arguably the most severe complication, affects the brain and is, by far, the most difficult to treat. This stage can be life-threatening. Few symptoms of tertiary syphilis are:
- blindness
- deafness
- mental illness
- memory loss
- destruction of soft tissue and bone
- neurological disorders
- meningitis
- heart disease
- neurosyphilis
Introduction
Syphilis is one of the better-known sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Like other STDs syphilis can be spread by any type of sexual contact. Syphilis can also be spread from an infected mother to the fetus during pregnancy or to the baby at the time of birth. It is caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum and is common in both male and female. It usually starts by causing painless sores, called chancres or rashes on the genitals, mouth, anus, or rectum. According to the symptoms seen and the duration of the disease syphilis has been divided into three stages. It can cause serious damage to various organs if not treated properly.
Causes
Syphilis is transmitted from syphilis infected persons to healthy ones through genital, oral or anal sex or from infected mother to fetus during pregnancy or to new-born baby while giving birth. Syphilis is caused by spiral shaped bacterium Treponema pallidum where the spiral shape allows it to burrow into mucous membranes or enter through minute breaks in the skin. Syphilis doesn’t pass through toilet seats, shared utensils or casual contact. Less commonly, syphilis can be passed through kisssing if broken skin comes into contact. The factors that can increase a person’s risk of infection can be listed as below :
Symptoms
The symptoms of syphilis are different in different stages of infection which are divided into three categories as below :
Diagnosis of syphilis
There are two types of tests used to diagnose syphilis : treponemal tests and non-treponemal tests. Treponemal tests identify antibodies to the causative organism and non-treponemal tests identify the body’s response to the infection but not to the organism itself. The blood tests used to screen for syphilis are called VDRL and Rapid Plasminogen Reagent (RPR) tests. These tests must be followed by a treponemal test.
Treatment of syphilis
Syphilis can be treated with antibiotics. Penicillin IM is considered the drug of choice, but other antibiotics like doxycycline, tetracycline, azithromycin, should be used for a person who is allergic to penicillin.
Actually, penicillin is the treatment of choice for syphilis in all stages. Treatment with penicillin is safe during pregnancy too. Treatment kills the bacteria and prevents further organ damage, but will not reverse damage to the organs that has already occurred.
Preventive measures of syphilis
There is no vaccine available to prevent syphilis. Safe-sex practices, including condom use, can only prevent syphilis. But if the infectious chancre is located in a body are unprotected by a condom then only condom will not work. Washing or cleansing after sexual activity cannot prevent the infection. Neonatal syphilis is preventable by treating the mother early in her pregnancy.



Send us your feedback on this article