Cirrhosis of Liver
- Chronic viral hepatitis B and C: both are blood borne infection. Hepatits B is also transmitted sexuallay, and from mother-to-child.
- Chronic heavy alcohol use.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Drugs: Medication, isoniazid.
- Inflammatory condition of liver & bile ducts: Biliary cirrhosis.
- Genetic disorders of metabolism such as Hemochromatosis (excess iron) & Wilson disease (excess copper).
- Diseases of heart (right heart failure) or pericardium (constrictive pericarditis).
- Heavy alcohol use.
- History of jaundice or hepatitis, blood transfusion or injection drug use.
- Family history of Jaundice, hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- Feeling tired, loss of appetite.
- Jaundice.
- Swelling of abdomen or legs.
- See Physician immediately if
- Abnormal bleeding: vomiting blood, black tarry stool, red blood in stool; or
- Change in personality, confusion.
- Blood test: To check blood count, liver function, cause of cirrhosis.
- Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scan- shows small and scarred and nodular liver.
- Liver biopsy is needed to identify the cause of cirrhosis.
- Stop alcohol use.
- Stop medicine(s) that is toxic to liver.
- Treatment of hepatitis and other causes of cirrhosis.
- Diuretics to remove fluid and salt from the body.
- Limit fluid and salt intake.
- Removing fluid by needle (Paracentesis).
- Treatment of infection like spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP).
- Vitamin K.
- Replacement of clotting factors by Fresh frozen plasma infusion.
- Management of esophageal varices (see Esophageal varices).
- Gut decontamination by Antibiotics, Osmotic laxative (Lactulose).
- Nutritional support, electrolyte and fluid balance.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Get treated for hepatitis B, C or other causes of cirrhosis.
- If negative for Hepatitis B, get vaccinated.
- Regular check up to detect complication at earlier stage and its treatment.
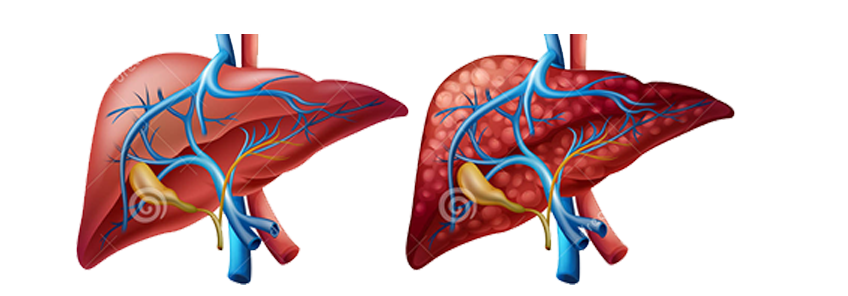
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic slowly progressive condition where normal liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue. The scar tissue is the final result of injuries to the liver by various substances. The destruction of normal liver tissue leads to reduced synthesis of proteins needed for the body, reduced clotting factors needed for blood coagulation. Similarly, toxins produced in the body that are normally removed by the liver accumulate in the body, which can lead to confusion and coma. The scar tissue blocks the blood flow through the liver and causes pressure in the blood vessels to rise that lead to buildup of fluid (ascites) in the abdomen. These enlarged blood vessel (esophageal varices) can rupture causing severe bleeding which could be fatal. Patients with cirrhosis are more susceptible to side effects of medication, and prone to infection and kidney failure. Cirrhosis can lead to liver cancer. It is a serious medical condition and a cause of premature death.
Causes/Risk factors:
Cirrhosis is the end result of many diseases or conditions. Some conditions are-
Symptoms/when to seek medical care:
Cirrhosis may not exhibit any symptoms until very late. So seek medical care if you are at risk for developing cirrhosis, particularly if you have:
When symptom occur, they could be:
Diagnosis
History, physical exam and labs test are used to diagnose cirrhosis, its cause and complication:
Treatment
Treatment of this condition depends on the cause and complication of cirrhosis.
Treatment of cause of cirrhosis
Treatment of complication of cirrhosis
Ascites (abnormal fluid collection in abdomen):
Abnormal bleeding:
Encephalopathy (confusion, change in personality):
Supportive treatment:
Liver transplant is the definite treatment for advanced cirrhosis.
Prevention of cirrhosis



Send us your feedback on this article