Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Helicobacter pylori infection:
- Majority of cases of gastric and duodenal ulcer are attributed to infection by H. pylori. It resides in the inner lining of the stomach wall, where it causes inflammation by the release of toxic compounds.
- Helicobacter pylori is present in 30-60% of patients with gastric ulcers and nearly 70% of patients with duodenal ulcers. In developing countries, about 80% of the population may be infected with this bacteria by the age of 20 years.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Regular use of painkillers like ibuprofen, naproxen, ketorolac etc. on high dose can cause ulcers. Factors such as advanced age, simultaneous use of steroids will make you more prone towards developing an ulcer.
- Too much acid production: Diseases that increase acid production in the stomach can cause peptic ulcer disease. One of such disease is called zollinger-ellison syndrome.
- Smoking: Smoking increases your risk of ulcer. It delays healing of the ulcer and medicines to treat the disease become less effective if you smoke. It also increases the risk of ulcer perforation.
- Other risk factors : Heavy alcohol drinking, family history of PUD, old age, and concomitant use of oral steroids are also associated with higher risk of having a PUD.
- Pain: a burning pain felt in the upper abdomen is the most common symptom of PUD. Pain is felt more during empty stomach, worse at nights and may be relieved by eating food.
- Bleeding : the ulcer can erode into a blood vessel and cause bleeding which could be life threatening. It could present as dark stool or vomiting of blood.
- Perforation: ulcer could erode all the way through the wall and cause perforation. It presents with a sudden severe and sharp pain in the abdomen, different from regular pain of PUD. This needs an emergent surgery.
- Obstruction: Scarring leading to intestinal obstruction resulting in nausea/vomiting and weight loss.
- Tests to diagnose H. pylori infection: your doctor will order a blood test or a stool test or a breath test to diagnose the infection. It depends on local availability of the test. If the test is positive you will need treatment with antibiotics.
- Tests to visualize the ulcer:
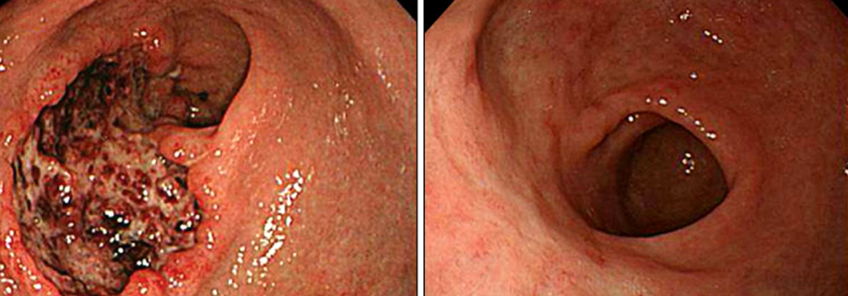
- Endoscopy is done to visualize the ulcer. It is particularly helpful in identifying lesions too small to detect by X ray examination. Your doctor also can take a biopsy to rule out cancer during endoscopy..
- Large ulcer can sometimes be diagnosed by barium swallow. In barium swallow, mixture of barium and water is swallowed followed by the X ray. Ulcer areas coated by barium can be seen on the X ray. Both gastric and duodenal ulcers appear as craters with well defined margins on the X ray examination.
- Lifestyle modification: Everyone who has PUD should stop smoking cigarettes, limit alcohol intake and avoid excessive nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID). Healthy diet with fruits and vegetables may help in healing of the ulcer.
- Medicines: You will need two groups of medicine. One group is a set of three antibiotics that you will take for 2-3 weeks to treat the H. pylori infection. The second group is of acid lowering medicines like ranitidine and pantoprazole. Antacids are taken to relieve the pain and burning sensation.
- Endoscopy or Surgery: If you have bleeding complications from ulcer, it can be stopped by endoscopic procedures and local instillation of medication at the bleeding ulcer. Occasionally bleeding might be so severe that you might need surgery.
Peptic Ulcer Diseases (PUD) are conditions where the lining of the stomach and the duodenum (first part of the small intestine) are damaged leading to the formation of open sores. The stomach and duodenum are in constant contact with gastric juice but the presence of a protective layer of mucus prevents the acids from damaging the lining. Whenever the balance between these two opposing actions is disturbed, an ulcer can develop. Although it is a common belief among people, spicy food does not cause peptic ulcer disease. But it can worsen the pain if you already have an ulcer.
Causes and risk factors
There are several causes for the peptic ulcer diseases, ranging from bacterial infection to genetic predisposition. Some are discussed below:
Symptoms/Complications
If you think you have peptic ulcer disease and you are losing weight, it is a danger sign of possible stomach cancer. You should see your doctor as soon as possible. Similarly dark stool is a danger sign of intestinal bleeding and you should contact your doctor immediately.
Diagnosis
PUD is diagnosed through the use of various tests and imaging/visualization methods. These include:
Treatment
PUD is treated with lifestyle modification, medicine, endoscopy or surgery.



Send us your feedback on this article