Hyperuricemia
- Chronic kidney disease
- Drugs/toxins- low dose Aspirin, Thiazide & Loop diuretics. Cyclosporine, Alcohol
- Obesity
- Primary underexcretion (no cause identified)
- Diet high in purine content
- High blood cell turnover, example blood cancer
- Drug/toxins: chemotherapy complications(Tumor lysis syndrome), Excess alcohol
- Obesity
- Inherited condition with enzyme deficiency
- Primary overproduction (no cause identified)
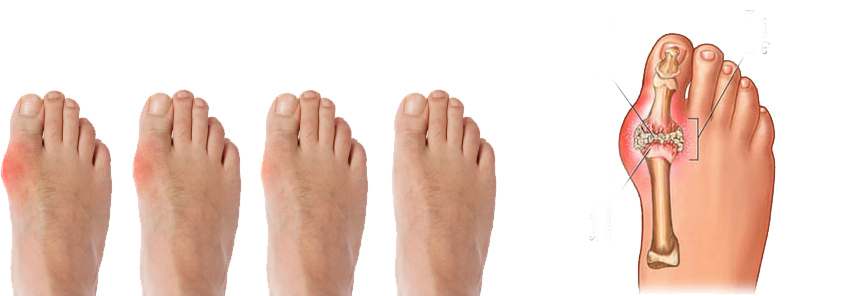
- Gout: sudden onset of joint pain, swelling usually involving single joint, commonly the great toe.
- Kidney stone: flank pain, blood in urine and nausea vomiting
- Tophi: deposition of uric acid in soft tissue
- Symptoms due to underlying cause: example weight loss due to cancer
- Blood tests: serum uric acid, blood counts, renal function tests, liver function tests, glucose, electrolytes, calcium and phosphate level
- Urine tests: urinary uric acid excretion,
- Imaging: X-ray, CT Scan, renal sonogram
- Joint aspiration in gout
- Avoid alcohol
- Weight loss, regular moderate physical exercise, low purine diet
- Consult your physician for alternate medicine (that does not increase uric acid) when possible
- Gout is treated with either nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Indomethacin, or Colchicine or glucocorticoids (Prednisone). Gout in a single joint can be treated with steroid injection into the joint
- Once acute attack of gout is controlled, uric acid lowering medicine (Allopurinol) is started.
- In patients with tophi, long term uric acid lowering therapy is needed.
- Avoid foods high in purine such as red meat, organ meat (liver, kidney), and seafood (sardine, anchovies, tuna).
- Stay hydrated, drink adequate water.
- Avoid alcohol
- Treatment of underlying cause
- Avoid medicine that increase uric acid
- Intravenous hydration prior to chemotherapy
Blood uric acid level above normal range is called hyperuricemia. Uric acid is formed in the liver when body breaks down purines and is excreted by the kidneys. Purines come from diet and our body. Purine rich diets are red meat, organ meat (liver, kidney), seafood (sardines, anchovies), beer, dried beans and peas, spinach, mushroom etc. Either excessive production or reduced excretion of uric acid leads to hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia may remain asymptomatic or cause symptoms by uric acid deposition in different tissues for example gouty arthritis (joint inflammation due to urate crystal deposition), kidney stone or tophi (deposition of uric acid in soft tissue).
Cause/Risk Factor
Reduced excretion or excess production of uric acid due to several conditions cause hyperuricemia:
Reduced excretion- is responsible for most of the hyperuricemia
Increased production
Symptoms
High uric acid does not always cause symptoms. When it does, it may cause some of the following symptoms:
Diagnosis
Hyperuricemia is diagnosed during evaluation of condition that cause high uric acid like chronic kidney disease. And when person has symptoms related to high uric acid level.
History, physical exam and lab tests are used diagnose high uric acid and its complication(s).
Treatment
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia: is managed with lifestyle modification and treatment of underlying cause. Drug to lower uric acid is usually not needed.
Symptomatic Hyperuricemia
Prevention of Hyperuricemia



Send us your feedback on this article