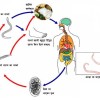
Tag: blood cell , cough , diarrhea , Fever , immunology , infectious disease , t lymphocytes , weight loss
-
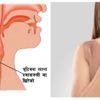
Difficulty swallowing (Dysphagia)
Dysphagia is the inability or difficulty in swallowing food or liquid. Normally, muscles in the throat (pharynx) and esophagus (food pipe) contract rhythmically to move food and liquids from mouth to stomach. Dysphagia occurs when there is a narrowing or lack of coordination of movem
-
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix. Appendix is a small, finger-shaped tubular structure attached to the large intestine located at the right side of lower abdomen. There is no known function of appendix in human body. When infected with bacteria or due to the blockage, the appendix gradually swells and g
-
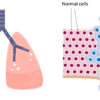
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer (Bronchogenic carcinoma) is the most common type of cancer worldwide and a leading cause of cancer death for both men and women. Lung cancer occurs when the normal cells of lungs abnormally change their characteristics and grow uncontrollably. Lung cancers may be
-
Fever
Definition A fever or pyrexia is a rise in body temperature above normal and often indicates an illness. Average normal body temperature is 98.6oF but it can range between 97 and 99.5
-
Cough
Cough is our body’s protective response to the presence of irritants in the airway. It is a reflex action caused by the stimulation of the nerve endings in the respiratory tract by stimuli such as allergen, microbes, foreign body or excessive mucous. After the stimuli reaches the bra
-
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs caused by a variety of germs. These germs reach the air sacs (lowest part of airways) after inhalation, overcoming body's normal defense mechanism like nasal hairs, mucus and cough which are weakened by smoking or dust inhalation. Once in the lungs,
-
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It can affect any organ in the body but lungs (Pulmonary TB) are the most common site of infection. Other common sites of infection are bones, lymph nodes, kidneys, uterus, brain (meninges), skin, etc. Tuberculosis i
-
Ascariasis
Ascariasis is infestation of humans intestine by roundworm (Ascaris lumbricoides). The roundworm may reside in the guts for 6 to 24 months. The eggs are passed into the stool and under warm, shady, moist conditions they can survive for up to 10 years. The infection is transmitted by in
-
Weight Loss
Weight loss that is meaningful clinically (in relation to your disease) is the loss of more than 5% of usual body weight over a six-month period. This arbitrary cut-off needs to be considered carefully as this does not tell about whether the given weight loss is due to loss of body fat (
-
Sore Throat
Sore throat (Pharyngitis & Tonsillitis) refers to pain, irritation or itchiness of the throat resulting from inflammation of the lining of throat and tonsils. It is common infection in children, but can affect people of any age. Symptoms include dryness of throat, swollen glands in
-
Red Eye
When the white part of eyes appears red, it is called a red eye. It is caused by dilatation of local blood vessels due to inflammation usually from either infection or irritation. Red eye can be a manifestation of local eye pathology or a sign of systemic disease. Red e
-
Coughing up Blood
Coughing up blood can be alarming, even in small amounts. But not all hemoptysis is serious or life-threatening. The blood may be mixed with the sputum or it could be frank blood which could be bright red, dark brown or pink and frothy. When you cough up blood, most of the time it is c
-
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus)
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a disease of immune system that can affect many organs in the body. Normally, the immune system produces proteins directed against infectious agents and protects us from infection. In SLE, however, your body produces antibodies that attack body’s o
-
Malaria
Malaria is a febrile, mosquito-borne disease caused by parasitic protozoa, Plasmodium. Four different species of Plasmodium cause malaria. The parasite is transmitted by bite of female Anopheles mosquito. It occurs mostly in high temperature areas - tropical regions and the Terai belt of Nepal. Infected female Anoph
-
HIV/AIDS
Introduction HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is the virus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). Infection by HIV weakens your immune system. When the immune system becomes too weak to fight, organisms that would otherwise not cause an infection in a normal person, that person is
-
Heart Failure
Heart failure means your heart is not able to pump out sufficient amount of blood into the rest of the body. It does not mean that your heart has stopped to beat which is called “cardiac arrest” (see Heart Attack for more informat
-
Diarrhea
Diarrhea is defined as increased frequency of defection (more than 3 per day) with excessive or abnormally loose consistency. Stool weights more than 200g/day are sometimes used to define diarrhoea but in the absence of abnormal consistency, weight alone is not an ideal indicator as bowel weight is influenced by high f
-
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus (commonly called diabetes) is a chronic disease where your blood sugar levels are persistently high. There is an important hormone called insulin in our body that keeps the blood glucose level within normal range. Insulin is produced by pancreas which is a gland located behind the stomach between the
-
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is a chronic condition of the lungs that causes difficulty in breathing. It is caused by long standing exposure to irritant gas or particles most commonly by cigarette smoking. In developing countries indoor smoke exposure from firewood burning also is an important risk factor.
-
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease that affects your airways (windpipe). The windpipe is inflamed, narrowed and swollen that causes difficulty in breathing now and then. A person with asthma has no difficulty in breathing most of the time except during an asthma attack. As
-
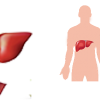
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Liver is one of vital organs and largest internal solid organ. Liver has large blood supply and functions as a chemical factory removing many unwanted substances from the body. This exposes liver to many insults including infections, drugs or
-
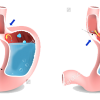
Gasteroesophageal Reflux Disease
Gasteroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is also known as acid reflux. GERD occurs is when stomach contents leak backwards (called “reflux”) into esophagus and cause symptoms or complications. Reflux is a normal process in infant, child or adult, but when it causes troublesome s
-
Diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infectious disease caused by bacteria Corynebacterium diphtheriae. The infection affects the respiratory passage leading to sore throat and breathing difficulties. The disease produces a
-
Allergy
Allergy is a conditions where your body abnormally reacts to foreign substances that normally should not produce any reaction. These substances are called allergens. Your immune system, which is responsible for protection of the body against external agents, recognizes these allergens as “invaders” and produce prot
-
Cancer
Cancer is a disease of abnormal cell proliferation. In a healthy organs, cells divide and grow in a regulated and controlled fashion. When these cell start to divide and grow unpredictably and uncontrollably, it develops into a lump know as tumor. These groups of abnormal cell can infiltrate causing destruction of surr
-
Amoebiasis/Giardiasis
Amoebiasis is an infection of gastrointestinal tract caused by an intestinal parasite called Entamoeba histolytica. It causes dysentery, liver abscess and rarely affects lungs, heart and brain. It occurs everywhere in the world but especially in the areas where there is poor sanitation and poor socioeconomic status. Th
-
Acid Reflux Disease
When we eat food, it travels through the mouth to the food pipe (esophagus) and then to the stomach. Once in the stomach, food cannot come back up into the esophagus under normal conditions because of the presence of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). LES is a group of fiber muscle rings at the lower end of the food